Hernia
What Size Hiatal Hernia Needs Surgery?
by admin
18th August 2023
6 minutes read
Hernias are medical conditions characterized by a protrusion or bulge of any tissue or organ through a weakened or damaged muscle wall, breaking the natural barrier. They manifest as small, painless swelling usually seen in your abdominal area, groins, pelvic or lower chest. Hernias most often occur due to excessive strain over the muscles or tissue walls, with an increased likelihood of family history, damage or injury, multiple pregnancies, smoking, obesity (overweight), and chronic (long-lasting) cough or constipation.
Depending on their location, there are different types of hernias, namely- inguinal, hiatal, ventral, umbilical, femoral, and incisional hernias, that present with different signs and symptoms.
This blog will explore hiatal hernia and when surgery to correct a hernia should be performed.
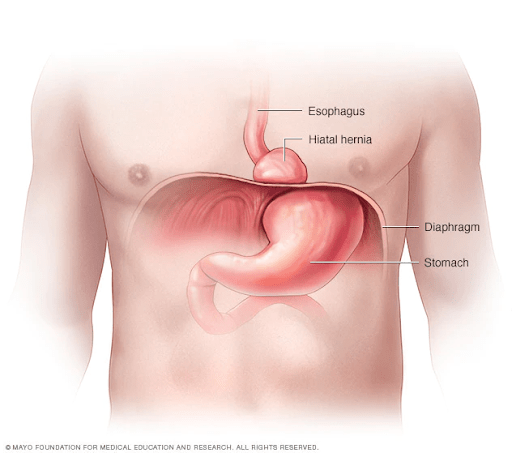
What is Hiatal Hernia?
A hiatal hernia is a condition that occurs when a part of your stomach pushes upward through the diaphragm muscle into your chest. The most common cause of hiatal hernia is an abnormal increase in pressure within your abdominal cavity. This can affect people of any age and gender and usually do not exhibit any symptoms, however if it grows in size it can lead to the symptoms of GERD (Gastroesophageal Reflux disease). GERD occurs when digestive juices move from your stomach back into the esophagus (reflux or regurgitates). Symptoms of hiatal hernia include: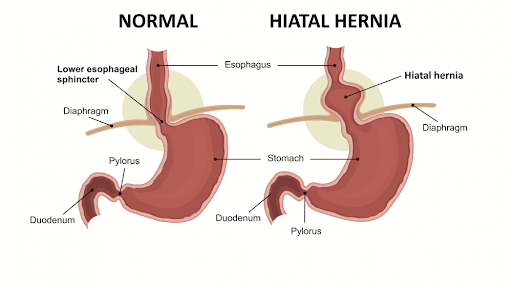
- Heartburn
- Nausea and vomiting
- Bitter taste at the back of your throat
- A feeling of burning sensation in the chest or throat
- Abdominal bloating
- Discomfort or pain in the stomach or esophagus
- Chest pain
What Size Hiatus Hernia Needs Surgery?
If the hiatus hernia is small without causing any obvious pain or discomfort, you would not require any surgery. But most often, hernias grow larger in size and lead to serious complications that require medical treatment.
Generally hernias that are smaller than 5 cm (2 to 3 inches) can be managed through lifestyle choices (weight loss, dietary changes) and medication. You are likely to experience symptoms with large or moderate-size hiatal hernias (more than 7 cm), which require a surgical intervention. Symptoms of hernia obstruction and strangulation like severe pain, fever, nausea, vomiting, constipation, acid reflux, heartburn, chest pain, and shortness of breath negatively impact your quality of life.
The surgical management of hernia can be conducted through open, laparoscopic or robotic approach and the main aim is the reduction of the hernia sac and tensionless closure of the hiatal defect. Type 1 and 2 hiatal hernias do not require a surgical treatment and can be managed with non-surgical methods, while Type 3 hiatal hernias require surgery if they become symptomatic, and type 4 hiatal hernias are larger hernias with increased complications that are usually repaired through surgery. If left untreated, hiatal hernias can cause complications of obstruction and strangulation.
Types of Hiatus Hernia
Hiatal hernia are of many types depending on their size, which help to determine the need for a surgical intervention. Hernias are considered to be small when their size ranges between 2 to 3 cm and medium when the size ranges between 4 to 5 cm. Hernias larger than 7 cm are considered to be ideal for a surgical repair.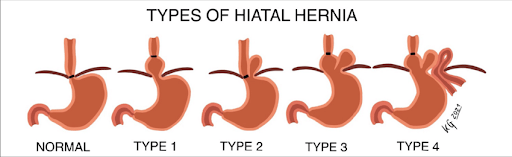
Hiatal hernias are classified into 4 types and it helps determine the type of treatment required.
-
Type 1 Hiatal Hernia
-
-
- This is the most common type of hernia also known as sliding hiatal hernia.
- These are usually small causing mild acid reflux which can be easily managed through lifestyle changes (dietary changes, weight loss, regular exercise, etc) and medications (like antacids)
- They do not require any surgical repair.
-
-
Type 2 Hiatal Hernia
-
-
- This usually occurs when the top part (fundus) of your stomach pushes through the esophageal hiatus (an opening in the diaphragm through which the esophagus passes from the thoracic into the abdominal cavity), but the GEJ (Gastroesophageal Junction) which is the connection between the stomach and esophagus (food pipe) is below the diaphragm.
- This type of hernia also does not require any surgical repair, until it becomes symptomatic.
-
-
Type 3 Hiatal Hernia
-
-
- This is a complicated type of hiatal hernia where the esophageal hiatus is compromised.
- This allows more of the stomach tissues to enter the hiatus and the GEJ shifts above the diaphragm.
- More of the stomach protrudes into your chest area.
- When type 3 hiatal hernia becomes symptomatic they usually require surgery.
-
-
Type 4 Hiatal Hernia
-
- This is a more serious type of hiatal hernia where the stomach and other surrounding structures like the spleen, pancreas, colon, etc, enter your chest cavity.
- This is mainly due to the defect in the abdominal cavity membrane which helps to hold the esophagus in place (pharyngoesophageal membrane).
- These hernias always require surgical repair owing to the risk of complications.
What are the Types of Surgeries that can Repair a Hiatal Hernia?
Surgical repair is necessary for larger hiatal hernias measuring more than 7 cm, that cause varying symptoms like obstruction and strangulation presenting with signs like- fever, nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, constipation, heartburn and acid reflux. There are many surgical approaches to treat a large hiatal hernia, which include:
-
Open or Traditional Hernia Surgery
-
-
- This is an old approach that requires larger incisions (cuts) to push back the protruded tissue to its original position and placing a mesh over it.
- It involves large, unsightly scarring with slow healing and prolonged recovery time.
-
-
-
- Advanced minimally-invasive (involves less bleeding and trauma) procedure that involves small keyhole-incisions to insert a laparoscope (device with a tiny camera and a light source) by projecting 3D images of the surgical site on a projection screen.
- There is less scarring, faster healing and speedy recovery with minimal post-op complications.
-
-
Robotic Hernia Surgery
-
- This approach is similar to the laparoscopic technique but using advanced robotic technology, where the surgeon is seated on a console to view the anatomic region of the operated area.
- There is less scarring with a faster recovery rate and minimal post-op complications.
Takeaway
Hiatal hernias occur when a part of your stomach is pushed into the cavity through your diaphragm causing a bulge or a lump. They present with symptoms like nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, heartburn, and acid reflux. Usually, Hiatal hernias smaller than 3 cm do not require surgery and can be managed with lifestyle changes and medications. Hiatal hernias larger than 7 cm in size impinge (press against) the surrounding structures like the spleen, pancreas, etc., causing severe complications (obstruction and strangulation) and affectING your quality of life. Such hiatal hernias must be surgically treated through an open, laparoscopic or robotic surgery.
For further doubts and queries, schedule an appointment with our team of healthcare specialists at Medfin.
Disclaimer:
The content on this site is the copyright of Medfin and is intended for informational and educational purposes only. This should not be considered as a substitute for medical and surgical expertise. Results from any treatments or surgeries are subjective to an individual patient and the type of procedure/ surgery performed. Please seek professional help regarding any medical concerns. Medfin will not be responsible for any act or omission arising from the interpretation of the content present on this page.
CATEGORIES
- ACL Reconstruction
- Anal Fissures
- Anal Fistula
- Appendicitis
- ASK A DOCTOR
- Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia
- Breast Lump Excision
- Cataract
- Circumcision
- Conditions & Diseases
- Cosmetology
- Covid-19
- Cure
- Endocrinology
- ENGLISH VIDEOS
- Eye Care
- Gallstones
- General Surgeries
- Government Schemes
- Gynaecology
- Gynecomastia
- Gynecomastia
- Health
- Health Insurance
- Hernia
- hindi
- Hip Arthoscopy
- Hip Replacement
- Hip Replacement Surgery
- Hydrocele
- Kannada
- Kidney Stones
- Knee Arthroscopic
- Laparoscopic
- LASER
- Latest Treatments
- Lifestyle
- Liposuction
- Medfin Stories
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedic
- Paraphimosis
- Patient Testimonials
- PCL Reconstruction
- Phimosis
- Piles (Hemorrhoids)
- Pilonidal Sinus
- Proctology
- Prostate Artery Embolization
- Rhinoplasty
- Second Opinion
- Total Knee Replacement
- Uncategorised
- Urology
- uterine artery embolization
- Uterine Fibroids
- Varicocele
- Varicose Veins
- Vascular
- VIDEOS






