Urology
What Is The Permanent Treatment For Recurrent Balanitis?
by admin
17th October 2023
7 minutes read
Introduction
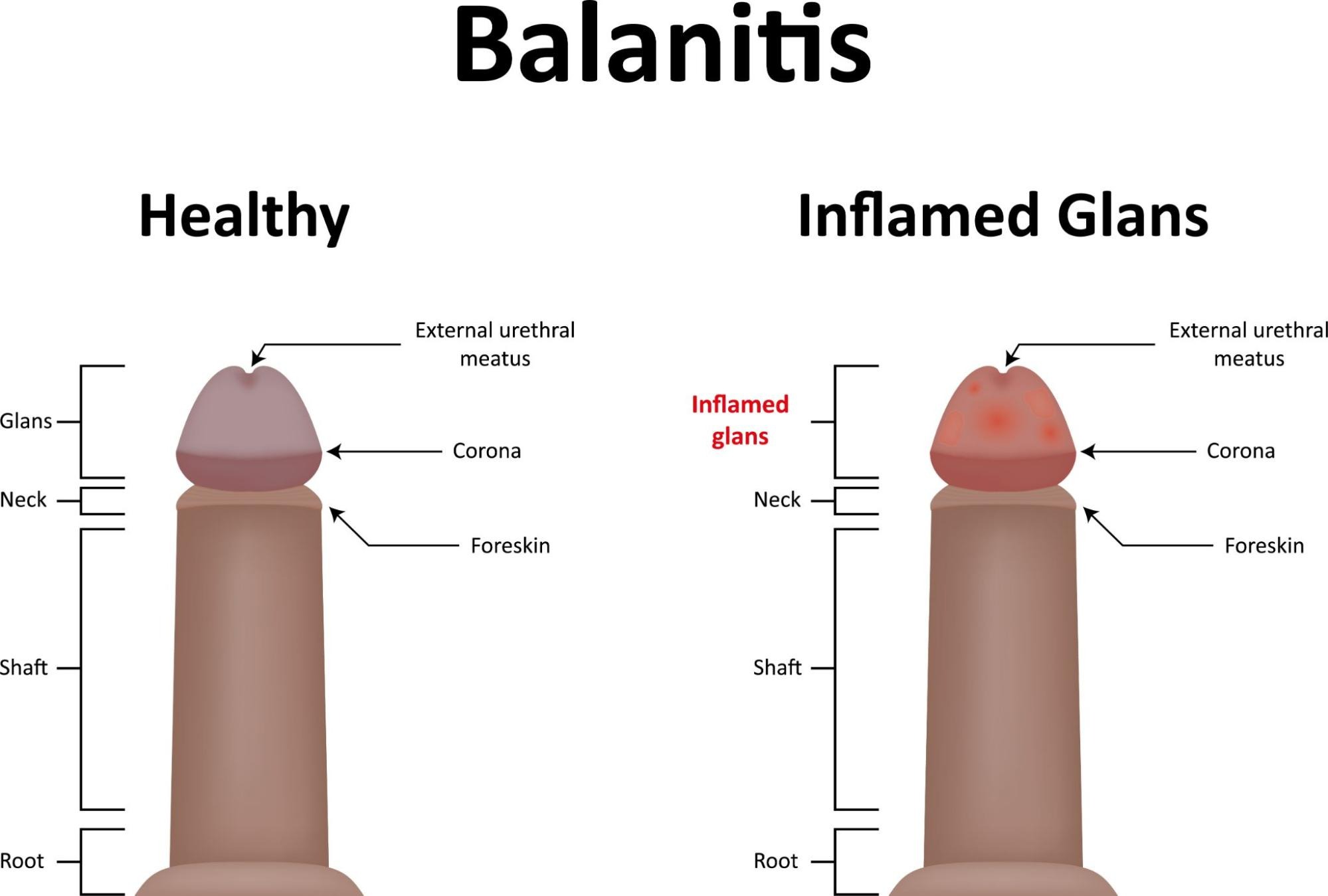
Balanitis is a common and uncomfortable medical condition that primarily affects men, causing inflammation and infection of the glans penis, or the head of the penis. While it is often referred to in various colloquial terms, such as “pennis infection”, it is important to recognize the formal medical term “balanitis” for accurate communication with healthcare professionals and when seeking appropriate treatment. Balanitis can be recurrent if not given proper care. Let’s understand the condition in detail here.
What is Recurrent Balanitis?
Balanitis is a medical term used to describe the inflammation of the glans penis, which is the rounded tip of the male genital organ. This condition is characterized by redness, swelling, and irritation of the glans penis and can be accompanied by symptoms such as itching, pain, and the presence of discharge in some cases.
Balanitis can result from various causes, including:
- Poor hygiene: Inadequate cleaning of the genital area can lead to the accumulation of smegma, It is a substance that can accumulate in the genital area when you do not maintain enough cleanliness. This can promote inflammation and infection.
2. Infections: Bacterial or fungal infections can cause inflammation of the glans penis, leading to balanitis. These infections may be the result of sexual contact, skin conditions, or other factors.
3. Skin conditions: Individuals with certain skin conditions like psoriasis or eczema may be more susceptible to developing balanitis.
4. Allergies or irritants: Exposure to irritants or allergens, such as harsh soaps or detergents, can lead to inflammation of the glans penis.
The symptoms of balanitis typically include the following:
- Redness: The glans penis (the rounded tip of the penis) becomes red and inflamed.
2. Swelling: Swelling or edema of the glans penis may be noticeable.
3. Itching: Itchiness in the genital area, particularly around the glans penis, is a common symptom.
4. Irritation: The affected area may feel sore or irritated.
5. Pain: Balanitis can cause discomfort or pain in the penis, particularly when urinating or during sexual activity.
6. Discharge: Some individuals may experience discharge, which can be white, yellow, or greenish in color and may have an unpleasant odor.
7. Difficulty retracting the foreskin: In cases where the foreskin is involved, it may become difficult to retract it over the glans penis.
8.Cracking or fissures: In some cases, the skin of the glans penis may develop small cracks or fissures.
It’s important to note that these symptoms can result from various causes of balanitis, including infections (bacterial or fungal), skin conditions, poor hygiene, or exposure to irritants or allergens. If you experience any of these symptoms, especially if they persist or worsen, it’s advisable to seek medical attention. A healthcare professional can diagnose the underlying cause of the balanitis and recommend appropriate treatment to alleviate the symptoms and prevent complications.
How to Get Rid of Recurrent Balanitis Permanently?
The potential for a permanent solution for balanitis depends on the underlying cause of the condition. Here are some considerations:
1. Circumcision:
In some cases, circumcision may be recommended as a permanent solution for recurrent balanitis, especially when the foreskin’s tightness (phimosis) is a contributing factor. Circumcision involves the surgical removal of the foreskin, which eliminates the risk of inflammation in that area.
2. Balloon Dilation or Preputioplasty:
In cases of phimosis without wanting to undergo circumcision, procedures like balloon dilation or preputioplasty can help widen the foreskin opening and reduce the risk of recurrence.
3. Treating Underlying Conditions:
If an underlying medical condition, such as diabetes or a skin disorder, is contributing to balanitis, managing and treating that condition effectively can reduce the risk of recurrence.
4.Lifestyle and Dietary Changes:
For individuals with diabetes, managing blood sugar levels through lifestyle and dietary changes can reduce the risk of infections, including balanitis.
It’s important to note that balanitis can result from a variety of causes, and the effectiveness of the permanent solution will depend on the specific case. To find the most appropriate solution, it’s essential to consult with a healthcare professional.
How to Prevent Balanitis?
Preventing balanitis involves good hygiene and, in some cases, addressing underlying health conditions. Here are some essential steps to help prevent balanitis:
Practice Good Hygiene:
- Gently clean the genital area, including the glans penis and the foreskin (if present), daily with warm water. Avoid using harsh soaps or irritants, as they can worsen the condition.
- Make sure to retract the foreskin (if applicable) and clean underneath it. Be gentle to avoid causing irritation.
Keep the Genital Area Dry:
After washing, thoroughly dry the genital area, including under the foreskin. Moisture can encourage fungal growth, which can lead to balanitis.
Avoid Irritants:
Avoid using harsh soaps, detergents, or perfumed products in the genital area, as they can cause irritation. Use mild, hypoallergenic soaps if necessary.
Use Condoms:
If you’re sexually active, using condoms can help prevent the transmission of infections that might lead to balanitis.
Treat Underlying Health Conditions:
If you have underlying medical conditions like diabetes, work with your healthcare provider to manage them effectively. Keeping your blood sugar levels in control can help prevent infections.
Practice Safe Sex:
Engaging in safe sexual practices can reduce the risk of sexually transmitted infections (STIs) that can lead to balanitis.
Prevent Tight Foreskin (Phimosis):
If you have a tight foreskin (phimosis), consider treatments like preputioplasty or circumcision to widen the foreskin opening. Consult a urologist to discuss your options.
Regular Check-ups:
Visit your healthcare provider for regular check-ups to monitor and manage any potential risk factors or early signs of balanitis.
Avoid Sharing Personal Items:
Do not share towels, undergarments, or other personal items that may harbor bacteria or fungi.
Preventing balanitis primarily involves maintaining good hygiene and being proactive about your sexual health. If you notice any symptoms of balanitis or are at risk due to an underlying condition, seek medical advice promptly. Early detection and appropriate treatment can help prevent the condition from worsening or recurring.
Conclusion
Balanitis is a medical condition that can cause discomfort and irritation in the male genital area. It is characterized by inflammation of the glans penis and can be triggered by various factors, including poor hygiene, infections, skin conditions, irritants, and more. However, with proper understanding and preventative measures, the risk of balanitis can be significantly reduced. Remember, the key to a healthy, comfortable, and balanitis-free life lies in education, proactive measures, and seeking professional guidance when needed. By taking these steps, individuals can reduce the risk of balanitis and ensure their overall well-being.
FAQs
Balanitis is not an STI, but it can be caused by the same pathogens that cause STIs. It can also result from various non-infectious factors like poor hygiene or skin conditions.
Balanitis can affect both circumcised and uncircumcised men, but it may occur less frequently in circumcised individuals.
If left untreated, balanitis can lead to complications such as phimosis (tight foreskin), scarring, and the spread of infection to other parts of the body.
Balanitis can occur at any age, but it is more common in young boys who may not have learned proper hygiene practices. However, it can affect men of all ages.
CATEGORIES
- ACL Reconstruction
- Anal Fissures
- Anal Fistula
- Appendicitis
- ASK A DOCTOR
- Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia
- Breast Lump Excision
- Cataract
- Circumcision
- Conditions & Diseases
- Cosmetology
- Covid-19
- Cure
- Endocrinology
- ENGLISH VIDEOS
- Eye Care
- Gallstones
- General Surgeries
- Government Schemes
- Gynaecology
- Gynecomastia
- Gynecomastia
- Health
- Health Insurance
- Hernia
- hindi
- Hip Arthoscopy
- Hip Replacement
- Hip Replacement Surgery
- Hydrocele
- Kannada
- Kidney Stones
- Knee Arthroscopic
- Laparoscopic
- LASER
- Latest Treatments
- Lifestyle
- Liposuction
- Medfin Stories
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedic
- Paraphimosis
- Patient Testimonials
- PCL Reconstruction
- Phimosis
- Piles (Hemorrhoids)
- Pilonidal Sinus
- Proctology
- Prostate Artery Embolization
- Rhinoplasty
- Second Opinion
- Total Knee Replacement
- Uncategorised
- Urology
- uterine artery embolization
- Uterine Fibroids
- Varicocele
- Varicose Veins
- Vascular
- VIDEOS






