ACL Reconstruction
Minimally Invasive ACL Reconstruction: Exploring the Benefits and Techniques
by admin
28th August 2023
8 minutes read
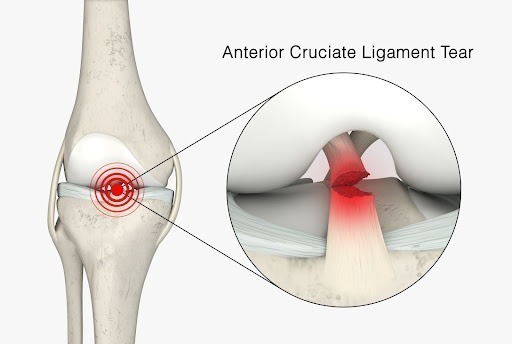
The anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) is a vital structure that stabilizes the knee joint. However, injuries to the ACL are common, especially among athletes involved in high-impact sports or activities that involve sudden changes in direction or pivoting. When the ACL is torn, it can lead to pain, instability, and reduced mobility. In such cases, ACL reconstruction surgery becomes a crucial option to restore the knee’s stability and functionality.
Traditionally, ACL reconstruction was performed through an open surgical approach, which involved large incisions and more extensive tissue disruption. However, with advancements in medical technology and surgical techniques, minimally invasive arthroscopic ACL reconstruction has emerged as a preferred method. In this blog, we will explore the benefits and techniques of minimally invasive ACL reconstruction.
Understanding ACL Tears and Symptoms
Before delving into the details of ACL reconstruction, it is essential to understand what ACL tears are and how they manifest. The ACL is one of the four primary ligaments in the knee joint and plays a crucial role in preventing excessive forward movement of the tibia (shinbone) in relation to the femur (thighbone).
ACL tears often occur due to sudden, forceful twisting or hyperextension of the knee joint. Common causes include abrupt changes in direction, jumping and landing incorrectly, direct blows to the knee, and accidents during sporting activities. Symptoms of an ACL tear may include:
- A popping sound at the time of injury
- Severe pain and swelling in the knee
- Instability and feeling of the knee “giving way”
- Limited range of motion
- Difficulty walking or bearing weight on the affected leg
- If you experience any of these symptoms after a knee injury, it’s essential to seek medical attention promptly.
The Importance of ACL Reconstruction
ACL tears seldom heal on their own due to the limited blood supply to the ligament. Consequently, untreated ACL tears can lead to chronic knee instability, increased risk of further knee injuries, and accelerated joint degeneration, which may result in early-onset osteoarthritis. To avoid these complications, ACL reconstruction is recommended for individuals who wish to return to an active lifestyle and sports participation.
The Evolution of ACL Reconstruction Techniques
The following are the various ACL reconstruction techniques:
a. Traditional Open Surgery:
In the past, open surgery was the standard approach for ACL reconstruction. It involved making a large incision to access the knee joint directly. Although this method was effective in stabilizing the knee, it was associated with significant post-operative pain, longer recovery times, and a higher risk of complications.
b. Minimally Invasive Arthroscopic ACL Reconstruction:
Arthroscopic ACL reconstruction represents a revolutionary advancement in knee surgery. Instead of making a large incision, the surgeon uses small incisions (less than half an inch) to insert an arthroscope—a thin, flexible tube with a camera and light attached to it. The arthroscope allows the surgeon to visualize the inside of the knee joint on a monitor and perform the procedure with precision.
Benefits of Minimally Invasive ACL Reconstruction
The following are the benefits of minimally invasive ACL reconstruction:
a. Smaller Incisions and Reduced Scarring:
Compared to open surgery, arthroscopic ACL reconstruction requires smaller incisions. As a result, patients experience less scarring, reduced risk of infection, and better cosmetic outcomes.
b. Less Tissue Damage:
Arthroscopic techniques involve minimal disruption of surrounding tissues, muscles, and ligaments. This leads to less trauma to the knee joint and faster recovery times.
c. Faster Recovery and Rehabilitation:
Due to the minimally invasive nature of the surgery, patients generally experience less pain and swelling after the procedure. Consequently, they can begin rehabilitation exercises and physical therapy earlier, promoting a faster return to normal activities.
d. Improved Visualization and Precision:
Arthroscopy provides surgeons with a magnified view of the knee’s internal structures, allowing for more accurate diagnosis and precise reconstruction of the ACL.
e. Reduced Hospital Stay:
With arthroscopic ACL reconstruction, patients may be able to go home on the same day as the surgery or after a short hospital stay, depending on individual recovery progress.
The Arthroscopic ACL Reconstruction Procedure
While specific surgical techniques may vary based on the surgeon’s preference and patient’s individual needs, the general steps of arthroscopic ACL reconstruction include:
a. Anesthesia:
The patient is placed under general anesthesia to ensure they remain unconscious and pain-free throughout the procedure.
b. Incision and Arthroscopy:
Small incisions are made around the knee joint to insert the arthroscope and surgical instruments. Saline solution is injected into the knee to create space and improve visibility.
c. ACL Debridement:
Any remaining fragments of the torn ACL are removed from the knee joint to prepare for the reconstruction.
d. Graft Harvesting:
A graft, which serves as a replacement for the torn ACL, is harvested from the patient’s body (autograft) or from a donor (allograft). Common autograft sources include the patellar tendon and hamstring tendons.
e. Graft Preparation:
The harvested graft is prepared to match the size and length of the original ACL.
f. Graft Placement:
The surgeon tunnels through the tibia and femur to create channels for the graft. The graft is then secured in place using screws, buttons, or other fixation devices.
g. Closure and Recovery:
After confirming the graft’s stability and proper placement, the incisions are closed, and the knee is bandaged. The patient is moved to a recovery area, where they are closely monitored as they wake up from anesthesia.
Choosing the Right Surgeon and Cost Considerations
When considering ACL reconstruction, it is crucial to find a qualified best orthopedic surgeon with experience in arthroscopic techniques. Look for a surgeon who is board-certified and has a proven track record of successful ACL reconstructions.
As for the cost of ACL reconstruction, it can vary based on factors such as the surgeon’s expertise, the location of the hospital or clinic, the type of graft used, and additional medical expenses. In India, ACL reconstruction surgery costs can be relatively lower compared to many other countries, making it an attractive option for international patients seeking high-quality medical care at a more affordable price.
Conclusion
Minimally invasive arthroscopic ACL reconstruction has transformed the landscape of knee surgery, offering patients numerous benefits over traditional open surgery. Through smaller incisions, reduced tissue damage, faster recovery times, and improved precision, this advanced technique has become the gold standard for treating ACL tears and restoring knee stability. If you have experienced an ACL injury, consult with a qualified orthopedic surgeon to explore the best treatment options and determine if arthroscopic ACL reconstruction is suitable for your condition. Remember, early intervention and proper care can significantly contribute to successful outcomes and a return to an active, healthy lifestyle.
How Can Medfin Help?
Medfin is a daycare surgery expert providing access to the latest surgical procedures and top doctors in your city at affordable prices. Medfin provides you access to top doctors and surgeons with 10+ years of experience. With Medfin, you can leave your hassles behind and focus on your health. From instant consultations to paperwork assistance, we have got you covered with everything. So why wait? Call us today!
FAQs
1. What are the symptoms of an ACL injury?
Symptoms of an ACL injury include a popping sound at the time of injury, immediate and severe pain, swelling within a few hours, instability in the knee (feeling of the knee “giving way”), and limited range of motion.
2. Can ACL injuries heal on their own?
ACL tears do not typically heal on their own due to the ligament’s limited blood supply. Conservative treatments like rest, physical therapy, and bracing may be sufficient for individuals with a partially torn ACL who do not require significant knee stability.
3. Is surgery necessary for ACL injury treatment?
For athletes and active individuals or those with significant instability and functional limitations, ACL reconstruction surgery is often recommended. It involves replacing the torn ACL with a graft from the patient’s own tissues (autograft) or a donor (allograft).
4. How long does it take to recover from ACL reconstruction surgery?
Recovery time varies, but most patients can begin walking with support a few days after surgery. Full recovery and return to sports may take six months to a year, depending on individual progress and adherence to rehabilitation guidelines.
5. What is the success rate of ACL reconstruction surgery?
ACL reconstruction has a high success rate, with many patients achieving excellent long-term outcomes and restoring knee function. However, success depends on factors like patient compliance with rehabilitation and the skill of the surgeon.
6. Can ACL injuries be prevented?
While ACL injuries cannot be entirely prevented, certain strategies can help reduce the risk. These include proper warm-up and stretching before physical activities, maintaining strong leg muscles, using proper landing and cutting techniques, and wearing appropriate footwear.
7. Is physical therapy necessary after ACL surgery?
Yes, physical therapy is a crucial aspect of ACL injury management and post-surgery rehabilitation. It helps strengthen the knee, improve the range of motion, and enhance functional recovery.
CATEGORIES
- ACL Reconstruction
- Anal Fissures
- Anal Fistula
- Appendicitis
- ASK A DOCTOR
- Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia
- Breast Lump Excision
- Cataract
- Circumcision
- Conditions & Diseases
- Cosmetology
- Covid-19
- Cure
- Endocrinology
- ENGLISH VIDEOS
- Eye Care
- Gallstones
- General Surgeries
- Government Schemes
- Gynaecology
- Gynecomastia
- Gynecomastia
- Health
- Health Insurance
- Hernia
- hindi
- Hip Arthoscopy
- Hip Replacement
- Hip Replacement Surgery
- Hydrocele
- Kannada
- Kidney Stones
- Knee Arthroscopic
- Laparoscopic
- LASER
- Latest Treatments
- Lifestyle
- Liposuction
- Medfin Stories
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedic
- Paraphimosis
- Patient Testimonials
- PCL Reconstruction
- Phimosis
- Piles (Hemorrhoids)
- Pilonidal Sinus
- Proctology
- Prostate Artery Embolization
- Rhinoplasty
- Second Opinion
- Total Knee Replacement
- Uncategorised
- Urology
- uterine artery embolization
- Uterine Fibroids
- Varicocele
- Varicose Veins
- Vascular
- VIDEOS






