Gynecomastia / Gynecomastia
When is Gynecomastia Bad Enough to Get Surgery?
by admin
31st August 2023
7 minutes read
Introduction
Gynecomastia, a medical condition characterized by the enlargement of breast tissue in males, can be a distressing experience for those affected. While it is generally not harmful, it can significantly impact a man’s self-esteem, body image, and overall quality of life. Gynecomastia may develop during puberty, due to hormonal imbalances, or as a result of other underlying health conditions. In some cases, lifestyle factors such as weight gain or the use of certain medications may also contribute to its development.
For many men, the management of gynecomastia starts with non-surgical treatments such as lifestyle changes, hormone therapy, or medication. However, in more severe cases where conservative methods fail to yield satisfactory results, gynecomastia surgery may be considered. In this detailed blog, we will explore the various aspects of gynecomastia, its causes, treatment options, and when surgery becomes a viable and beneficial solution.
Understanding Gynecomastia
What is Gynecomastia?
Gynecomastia is the benign enlargement of male breast tissue, leading to the appearance of breasts resembling those of a female. This condition can occur at any age but is more common during puberty and middle age. It is essential to differentiate between gynecomastia and pseudo-gynecomastia, which is caused by excess fat accumulation in the chest area. The latter can often be addressed through lifestyle changes such as diet and exercise, without the need for surgery.
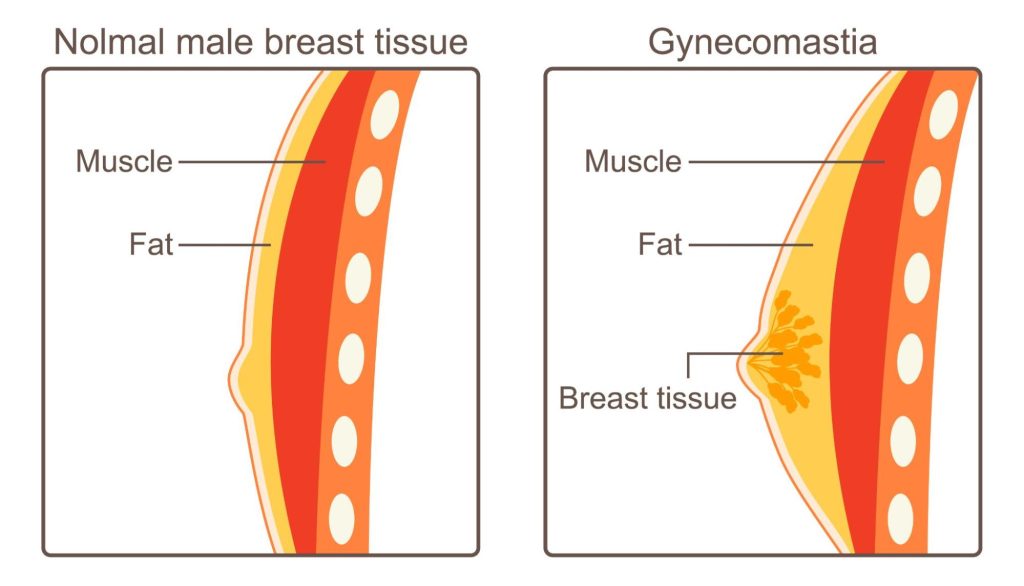
Types of Gynecomastia
There are several types of gynecomastia, each with its unique causes and characteristics. These include physiological gynecomastia (caused by hormonal imbalances during puberty), pathological gynecomastia (due to underlying medical conditions), and gynecomastia associated with weight gain or obesity. Understanding the type of gynecomastia a patient has is crucial for determining the appropriate treatment approach, including the consideration of surgery.
Non-Surgical Gynecomastia Treatments
Gynecomastia Treatment without Surgery
In mild to moderate cases of gynecomastia, non-surgical approaches are often the first line of treatment. These may include lifestyle changes, dietary modifications, exercise, and the discontinuation or adjustment of medications that may be contributing to the condition. Additionally, hormonal therapy and medications, such as selective estrogen receptor modulators (SERMs) or aromatase inhibitors, may be prescribed to reduce breast tissue enlargement.
Gynecomastia and Weight Loss
For some individuals, gynecomastia may be exacerbated by excess body weight. Weight loss, achieved through a combination of a balanced diet and regular physical activity, can help reduce the size of male breasts in such cases. However, it is essential to note that weight loss alone may not fully address glandular breast tissue, and surgical intervention might still be required for optimal results.
Liposuction for Gynecomastia
Liposuction is a minimally invasive procedure that can be used to remove excess fat from the chest area in cases of pseudo-gynecomastia. This technique is effective for patients whose enlarged breasts are primarily composed of fatty tissue. However, if glandular tissue is also present, liposuction alone may not be sufficient, and a combination of liposuction and surgical excision may be necessary.
When to Consider Gynecomastia Surgery
Psychological and Emotional Impact
Gynecomastia can have a profound psychological and emotional impact on affected individuals, leading to feelings of embarrassment, low self-esteem, and social withdrawal. It can affect their personal relationships, hinder physical activities, and even impact their professional life. In cases where non-surgical treatments have failed to provide relief and the psychological toll becomes unbearable, surgery may be considered to restore self-confidence and improve overall well-being.
Persistent Gynecomastia after Puberty
In many cases, gynecomastia that develops during puberty resolves on its own within a couple of years. However, when the condition persists into adulthood, it is less likely to resolve spontaneously. For individuals whose gynecomastia has not improved over time, surgery might be the most effective and lasting solution to reduce breast tissue size and restore a more masculine chest contour.
Gynecomastia in Bodybuilders
Bodybuilders may be more susceptible to gynecomastia due to the use of anabolic steroids and other performance-enhancing substances. These substances can disrupt hormonal balance and lead to the development of male breast tissue. For bodybuilders who wish to address this issue and continue pursuing their fitness goals, gynecomastia surgery can be an option to achieve a more sculpted and proportional chest.
Medical Conditions and Gynecomastia
Certain medical conditions, such as liver disease, kidney failure, and hormone-secreting tumors, can cause gynecomastia. In such cases, treating the underlying condition is essential. However, surgery may be recommended if the breast enlargement is severe or if it does not improve after addressing the root cause.
Importance of Consulting a Gynecomastia Doctor
Before deciding on surgery, it is crucial for individuals with gynecomastia to consult with a qualified gynecomastia doctor or plastic surgeon. The doctor will evaluate the patient’s medical history, conduct a physical examination, and recommend appropriate treatment options based on the type and severity of gynecomastia.
Gynecomastia Surgery Procedure
1.Preparing for Surgery
The gynecomastia surgery procedure begins with a thorough consultation, during which the surgeon discusses the patient’s goals, medical history, and any concerns. The patient will be given pre-operative instructions to follow, such as avoiding certain medications, alcohol, and smoking.
2.Surgical Techniques
There are several surgical techniques used to treat gynecomastia, including liposuction, excision, or a combination of both. Liposuction is employed to remove excess fatty tissue, while surgical excision is necessary for glandular breast tissue removal. The surgeon will determine the most suitable technique for each patient’s unique situation.
3.Recovery and Aftercare
Following gynecomastia surgery, patients will be given post-operative care instructions, including wound care and wearing compression garments. Recovery time may vary, but most individuals can resume light activities within a few days and gradually return to regular activities in a few weeks. The surgeon will schedule follow-up appointments to monitor the healing progress.
Conclusion
Gynecomastia is a condition that can significantly impact a man’s physical and emotional well-being. While non-surgical treatments are often the first approach, they may not be sufficient for all cases. When gynecomastia causes significant distress or fails to respond to conservative measures, gynecomastia surgery can be a life-changing solution. By consulting with a qualified gynecomastia doctor and understanding the surgical options available, individuals with gynecomastia can make informed decisions about their treatment to achieve a more masculine and confident chest contour. Remember, the decision to undergo gynecomastia surgery should be made after careful consideration of the potential benefits and risks associated with the procedure.
How Can Medfin Help?
Medfin is a daycare surgery expert providing access to the latest surgical procedures and top doctors in your city at affordable prices. Medfin provides you access to top doctors and surgeons with 10+ years of experience . With Medfin, you can leave your hassles behind and focus on your health. From instant consultations to paperwork assistance, we have got you covered with everything. So why wait? Call us today!
FAQ’s
Risk factors for gynecomastia include hormonal imbalances during puberty, aging (decrease in testosterone levels), certain medications (e.g., antiandrogens, anabolic steroids), chronic liver or kidney disease, and obesity.
Yes, gynecomastia can sometimes be a sign of an underlying medical condition, such as hormonal disorders (e.g., hypogonadism, hyperthyroidism), tumors (testicular or adrenal), or liver and kidney diseases. It is essential to get a medical evaluation to rule out any potential underlying causes.
Diagnosing gynecomastia involves a physical examination and a review of medical history. Additional tests may be performed, including hormone level assessments (testosterone, estrogen), imaging studies (ultrasound, mammography), and sometimes a biopsy to rule out other conditions.
Like any surgical procedure, male breast reduction surgery carries some risks. These may include bleeding, infection, adverse reactions to anesthesia, scarring, changes in nipple sensation, and asymmetry in the chest area. However, these risks are generally low when the surgery is performed by a skilled and experienced plastic surgeon.
The surgical procedure for gynecomastia typically involves liposuction to remove excess fat and glandular tissue. In severe cases, surgical excision may be necessary to remove larger amounts of tissue. The surgery is usually performed under general anesthesia, and the duration can vary depending on the extent of the gynecomastia. Recovery time varies, but most patients can resume light activities within a few days and return to full physical activities within a few weeks.
CATEGORIES
- ACL Reconstruction
- Anal Fissures
- Anal Fistula
- Appendicitis
- ASK A DOCTOR
- Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia
- Breast Lump Excision
- Cataract
- Circumcision
- Conditions & Diseases
- Cosmetology
- Covid-19
- Cure
- Endocrinology
- ENGLISH VIDEOS
- Eye Care
- Gallstones
- General Surgeries
- Government Schemes
- Gynaecology
- Gynecomastia
- Gynecomastia
- Health
- Health Insurance
- Hernia
- hindi
- Hip Arthoscopy
- Hip Replacement
- Hip Replacement Surgery
- Hydrocele
- Kannada
- Kidney Stones
- Knee Arthroscopic
- Laparoscopic
- LASER
- Latest Treatments
- Lifestyle
- Liposuction
- Medfin Stories
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedic
- Paraphimosis
- Patient Testimonials
- PCL Reconstruction
- Phimosis
- Piles (Hemorrhoids)
- Pilonidal Sinus
- Proctology
- Prostate Artery Embolization
- Rhinoplasty
- Second Opinion
- Total Knee Replacement
- Uncategorised
- Urology
- uterine artery embolization
- Uterine Fibroids
- Varicocele
- Varicose Veins
- Vascular
- VIDEOS






