Gynecomastia / Gynecomastia
A Comprehensive Look at the Types of Gynecomastia Tissue
by admin
2nd August 2023
7 minutes read
Gynecomastia, the medical term for male breast enlargement, is an issue that can significantly impact a man’s confidence and physical comfort. However, not all gynecomastia is the same. This blog post delves into the various types of gynecomastia tissue and explores gynecomastia surgery, treatment, and recovery. By understanding these differences, men can better navigate the road to their desired physical appearance after male breast removal or man chest reduction surgery.
The Essentials of Gynecomastia
Before we dive into the types of gynecomastia tissue, let’s first understand the basics of the condition itself. Gynecomastia, affecting men across all ages, is typically marked by the enlargement of glandular tissue in the male chest. It’s not just a cosmetic concern; gynecomastia often comes with pain and tenderness in the chest area.
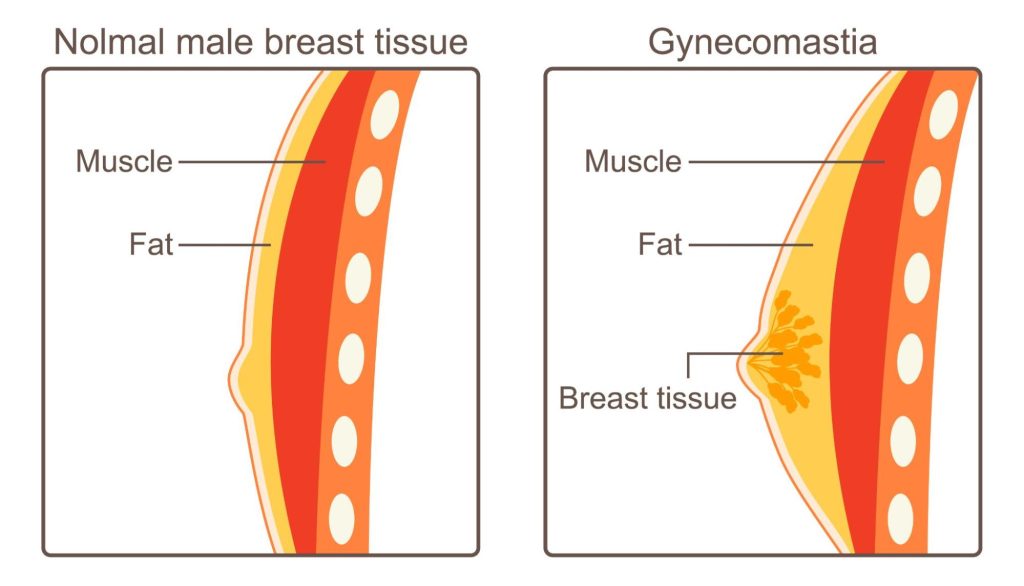
This condition can result from various causes such as hormonal imbalances, obesity, certain medications, or natural aging. It’s often categorized into three types based on the primary tissue involved: glandular gynecomastia, fatty gynecomastia, and mixed gynecomastia.
Glandular Gynecomastia
Glandular gynecomastia is a type characterized by an overgrowth of the glandular tissue in the chest, often triggered by hormonal imbalances. Men with this type have a firm, rubbery mass underneath the nipple area that can be felt distinctly. The enlargement may occur on one or both sides, resulting in an uneven chest appearance. Bodybuilders often experience this form of gynecomastia, also known as “bodybuilder gynecomastia,” due to the use of anabolic steroids which can disrupt hormone balance.
The primary treatment for glandular gynecomastia is surgery. Gynecomastia surgery for this condition usually involves removing the enlarged glandular tissue to achieve a flatter, more masculine chest contour. Patients generally report high satisfaction rates post-surgery, and the risk of recurrence is low as the glandular tissue has been entirely removed.
Also Read: Liposuction gynecomastia surgery
Fatty Gynecomastia
Fatty gynecomastia, also known as pseudo-gynecomastia, is a common form of gynecomastia, a condition marked by the enlargement of male breast tissue. However, unlike true gynecomastia, which involves the growth of glandular tissue, fatty gynecomastia is characterized by an increase in adipose (fatty) tissue in the chest area.
The primary cause of fatty gynecomastia is obesity, as excess fat deposits can lead to the appearance of larger breasts in men. It may also occur in men who’ve lost significant weight but still have remaining fat deposits in the chest area. The condition, while not life-threatening, can cause psychological distress and lower self-esteem due to societal perceptions of male body image.
Identifying fatty gynecomastia involves a thorough physical examination and history-taking by a healthcare provider. The enlarged area feels soft and is usually not confined to the area beneath the nipple, unlike glandular gynecomastia. It may also be more widespread across the chest.
The treatment for fatty gynecomastia primarily revolves around lifestyle modifications, including dietary changes and increased physical activity, aimed at overall weight reduction. In cases where these interventions do not lead to desired results, surgical options, such as liposuction or a more comprehensive surgical approach like male breast reduction, may be explored to remove the excess fat. However, to maintain the results post-surgery, it is essential to uphold a healthy lifestyle to prevent the recurrence of fat deposition.
Related Information: Nasal reconstruction surgery
Mixed Gynecomastia
Mixed gynecomastia is characterized by an overgrowth of both glandular and fatty tissue. This is the most common form of gynecomastia and often requires a combination of gynecomastia surgery and weight loss efforts for effective treatment.
In cases of mixed gynecomastia, a two-pronged approach is often taken. Firstly, liposuction may be used to remove excess fat, followed by excision to remove the glandular tissue. After surgery, maintaining a healthy diet and regular exercise regimen can help keep the chest contour in check and prevent recurrence.
Gynecomastia Treatment and Recovery
Regardless of the type of gynecomastia tissue, the decision to undergo male gynecomastia treatment should be made after careful consultation with a healthcare provider. The chosen approach should take into account the individual’s overall health, the type and severity of gynecomastia, and the potential risks and benefits of treatment.
For those who undergo gynecomastia surgery, the road to recovery usually includes wearing a compression garment to reduce swelling and support the new chest contour as it heals. Discomfort after surgery can be managed with prescribed medications. It’s also crucial to follow the surgeon’s instructions on wound care to minimize scarring.
Regular physical activity can generally be resumed after a few weeks, but activities that may strain the chest area should be avoided until the surgeon gives the go-ahead. It’s also important to monitor the chest area for any changes or signs of complications such as infection or bleeding.
Final Thoughts
The journey towards a more confident self can be a long one for many men with gynecomastia. But understanding the different types of gynecomastia tissue and their respective treatments can serve as a roadmap toward achieving the desired physical appearance.
Remember, whether it’s glandular, fatty, or mixed gynecomastia, there’s a suitable treatment option available. The key is to seek professional advice and make informed decisions about your health. With patience and proper care, men with gynecomastia can look forward to a flatter, more masculine chest contour and improved quality of life.
How Can Medfin Help?
Medfin is a daycare surgery expert providing access to the latest surgical procedures and top doctors in your city at affordable prices. Medfin provides you access to top doctors and surgeons with 10+ years of experience . With Medfin, you can leave your hassles behind and focus on your health. From instant consultations to paperwork assistance, we have got you covered with everything. So why wait? Call us today!
frequently asked questions (FAQ)
Gynecomastia tissue refers to the excess growth of breast tissue in males, leading to the appearance of enlarged breasts. It can occur due to hormonal imbalances, medications, certain medical conditions, or genetics.
Identifying the type of gynecomastia tissue may be difficult without a proper medical examination. However, you can try self-assessment by pinching the breast area around the nipple. If you feel a firm, button-like lump directly beneath the nipple, it suggests glandular tissue. If the area feels more widespread and relatively soft to the touch, it is likely to be fatty tissue. It is crucial to consult a healthcare professional to get an accurate diagnosis.
Yes, it is possible to have a combination of both glandular and fatty gynecomastia, known as mixed gynecomastia. This type of gynecomastia may involve excess breast gland tissue as well as an accumulation of fat in the chest area. The proportion of glandular and fatty tissue can vary from person to person, which is why an individualized approach to treatment is essential.
Glandular gynecomastia often requires surgical intervention for effective treatment. In cases where the enlargement is primarily due to the mammary gland, liposuction alone may not be sufficient. Surgical excision of the glandular tissue is usually performed through a small incision around the areola. This procedure is known as subcutaneous mastectomy or glandular excision.
Liposuction can be an effective treatment for fatty gynecomastia, especially when there is minimal glandular tissue involved. It involves the removal of excess fat using a cannula inserted through small incisions. However, if there is a significant amount of glandular tissue present, liposuction alone may not provide satisfactorily
CATEGORIES
- ACL Reconstruction
- Anal Fissures
- Anal Fistula
- Appendicitis
- ASK A DOCTOR
- Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia
- Breast Lump Excision
- Cataract
- Circumcision
- Conditions & Diseases
- Cosmetology
- Covid-19
- Cure
- Endocrinology
- ENGLISH VIDEOS
- Eye Care
- Gallstones
- General Surgeries
- Government Schemes
- Gynaecology
- Gynecomastia
- Gynecomastia
- Health
- Health Insurance
- Hernia
- hindi
- Hip Arthoscopy
- Hip Replacement
- Hip Replacement Surgery
- Hydrocele
- Kannada
- Kidney Stones
- Knee Arthroscopic
- Laparoscopic
- LASER
- Latest Treatments
- Lifestyle
- Liposuction
- Medfin Stories
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedic
- Paraphimosis
- Patient Testimonials
- PCL Reconstruction
- Phimosis
- Piles (Hemorrhoids)
- Pilonidal Sinus
- Proctology
- Prostate Artery Embolization
- Rhinoplasty
- Second Opinion
- Total Knee Replacement
- Uncategorised
- Urology
- uterine artery embolization
- Uterine Fibroids
- Varicocele
- Varicose Veins
- Vascular
- VIDEOS






