General Surgeries
Why do Lipomas occur?
by admin
31st July 2023
6 minutes read
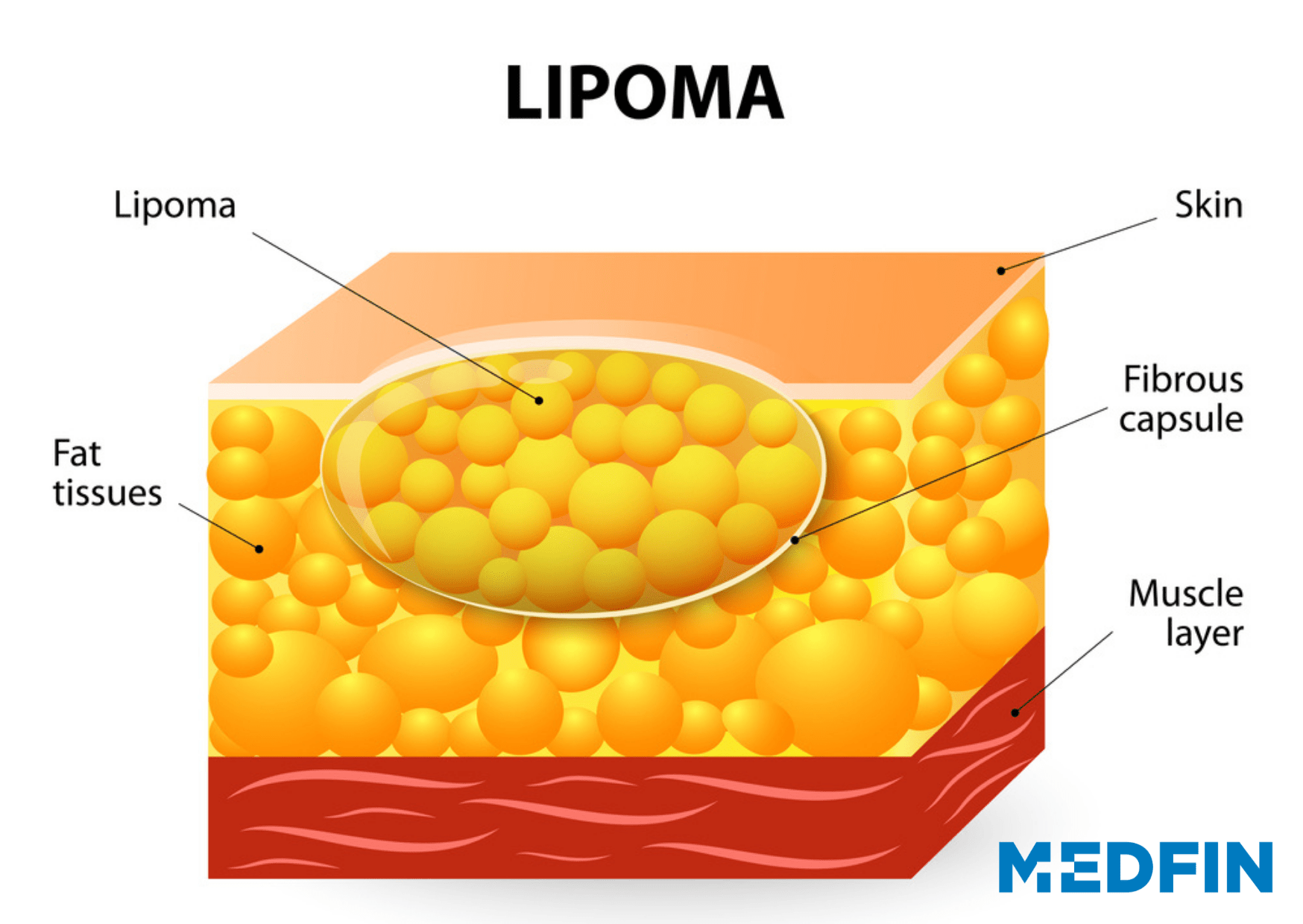
A lipoma is a lump of tissues that predominantly consists of fat cells. These are small (usually 2 to 3 mm in diameter) in size, move easily when you touch them, and are soft. Lipomas are most often painless swellings that can occur anywhere in your body between your skin and the muscle layer, but they commonly occur in the following areas:
- The forehead
- Lipoma on the Arms
- Legs
- Neck and shoulders
- Back
- Thighs
- Buttocks
These lumps are harmless and do not cause any serious medical problems, hence do not require any treatment. These are non-cancerous in nature, however, periodic monitoring is important to check the change in size and color to rule out malignancy (cancer-forming ability). Lipomas usually do not spread to other parts of the body, but sometimes they may be present in different areas which is known as Lipomatosis.
Let us explore why lipomas occur and what risk factors are associated with lipoma formation.
Why do Lipomas Occur?
Lipomas are slowly progressing lumps or nodular swellings mostly made up of fat cells. The exact cause of lipomas is not known. However,
-
- Lipoma is believed to be an inherited condition, meaning it runs in families. The condition is passed down through generations, and genetics plays an important role in developing lipomas. There is a high chance you would develop a lipoma if someone in your family has it.
- Research studies indicate that lipoma occurs in areas subjected to trauma or injury. The impact caused by high-intensity trauma and accidents predisposes the development of lipomas.
- Certain medical conditions cause multiple lipomas (Lipomatosis) in your body. These include:
-
Gardner’s syndrome
-
-
-
- It is a congenital (people are born with it) disease that causes multiple colon overgrowths (polyps), and various types of benign (non-cancerous), and malignant (cancerous) tumors.
- It is a rare disorder.
-
-
-
Dercum’s disease
-
-
-
- This is also known as Adiposis Dolorosa or Andre’s Syndrome.
- It is a rare autoimmune disorder that presents with painful lipomas in the torso, upper arms, and upper legs.
-
-
-
Madelung’s disease
-
-
-
- This rare lipid storage disorder (fat metabolism) leads to an unusual accumulation of subcutaneous fat deposits.
- This commonly occurs around the neck, shoulders, arms, hips, and thighs.
- The fat lumps either grow quickly over months or develop slowly over the years.
-
-
-
Cowden syndrome
-
-
-
- This inherited condition is characterized by multiple benign, tumor-like overgrowths known as hamartomas.
-
-
-
Hereditary Multiple Lipomatosis
-
-
- Also known as Familial Multiple Lipomatosis (FML).
- It is an inherited condition consisting of slow-growing nodules spread across the trunk and limbs.
-
What are the Risk Factors Associated With The Development of Lipoma?
Though the exact cause of lipoma is unknown or believed to be inherited, certain risk factors are associated with the condition. These include:
Age- Lipomas can occur at any age, and even at birth. However, they are more common during your 40s to 60s.
Gender- There is an increased incidence of lipomas in men than in women.
Obesity- When a person is obese (overweight), an increased fat accumulation may put you at a high risk of developing lipomas.
Diabetes- It is a condition characterized by increased blood sugar/glucose in the body. Type 2 diabetes is associated with the development of lipomas.
Liver disease- A liver disease like hepatic adenomas increases the risk of lipoma. They are also common in people with high cholesterol levels.
Alcohol abuse- Drinking a large amount of alcohol can lead to fat build-up in your liver, and also slow down your fat metabolism.
Soft tissue trauma- It is believed that trauma affecting the soft tissue releases certain inflammatory chemicals that are responsible to trigger the onset of lipoma formation.
Glucose intolerance- This causes obesity due to insulin resistance, which could indirectly lead to lipoma formation.
How Can You Prevent Lipoma?
Lipomas are soft, rubbery, painless lumps of fatty tissues that usually do not require treatment unless they are unaesthetic in appearance or cause extreme pain and discomfort. Since the exact cause is unknown, and it is believed that lipomas are inherited, it is not possible to prevent lipomas. However, you can reduce the occurrence by:
- Lowering the risk of certain medical conditions like Madelung’s disease, by limiting your alcohol consumption.
- Reducing your weight to burn out the excess fat present in your body.
- Exercise regularly and consume a healthy, nutritious diet.
- Controlling your blood sugar levels.
- Keeping a check on your cholesterol levels. Can Lipomas be Treated?
Lipomas are non-cancerous, slowly progressing, painless lumps that usually do not require any treatment. Periodic monitoring is however necessary to observe any changes occurring in the size and colour of the lipoma, to rule out malignancy.
Treatment is required when your lipomas cause severe pain and discomfort due to pressing against the nerve and blood vessels running through it. Multiple lipomas are also recommended to be removed if they are aesthetically displeasing, or affect your quality of life. Treatment of lipomas includes:
- Surgical excision – The lipoma is surgically removed completely through incisions made on the affected area.
- Steroid injections- Steroid injections are injected into the affected area that shrinks the lipoma.
- Liposuction- A large needle with a syringe is used and injected into the affected area to aspirate (suction out) the fatty tissue.
Takeaway
Many people happen to live with lipomas and never notice them. These lumps of fatty tissues can be annoying and unaesthetic, but they do not cause any medical problems.
What causes lipoma has always been a mystery, but they are believed to be inherited. Risk factors like Gardner’s syndrome, Cowden syndrome, diabetes, alcohol abuse, etc., increase the likelihood of lipoma formation.
Lipomas are most often benign and painless and do not require treatment unless they cause pain. Surgical excision of lipoma is the best treatment to remove them completely; they usually do not recur once removed.
If you have a lipoma and notice any changes such as sudden pain, enlarged size, or discoloration, contact our healthcare professionals at Medfin, for a complete examination and evaluation of your fatty lump.
Disclaimer:
The content on this site is the copyright of Medfin and is intended for informational and educational purposes only. This should not be considered as a substitute for medical and surgical expertise. Results from any treatments or surgeries are subjective to an individual patient and the type of procedure/ surgery performed. Please seek professional help regarding any medical concerns. Medfin will not be responsible for any act or omission arising from the interpretation of the content present on this page.
CATEGORIES
- ACL Reconstruction
- Anal Fissures
- Anal Fistula
- Appendicitis
- ASK A DOCTOR
- Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia
- Breast Lump Excision
- Cataract
- Circumcision
- Conditions & Diseases
- Cosmetology
- Covid-19
- Cure
- Endocrinology
- ENGLISH VIDEOS
- Eye Care
- Gallstones
- General Surgeries
- Government Schemes
- Gynaecology
- Gynecomastia
- Gynecomastia
- Health
- Health Insurance
- Hernia
- hindi
- Hip Arthoscopy
- Hip Replacement
- Hip Replacement Surgery
- Hydrocele
- Kannada
- Kidney Stones
- Knee Arthroscopic
- Laparoscopic
- LASER
- Latest Treatments
- Lifestyle
- Liposuction
- Medfin Stories
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedic
- Paraphimosis
- Patient Testimonials
- PCL Reconstruction
- Phimosis
- Piles (Hemorrhoids)
- Pilonidal Sinus
- Proctology
- Prostate Artery Embolization
- Rhinoplasty
- Second Opinion
- Total Knee Replacement
- Uncategorised
- Urology
- uterine artery embolization
- Uterine Fibroids
- Varicocele
- Varicose Veins
- Vascular
- VIDEOS






