Orthopaedic
What is ACL Surgery?
by admin
28th December 2023
10 minutes read
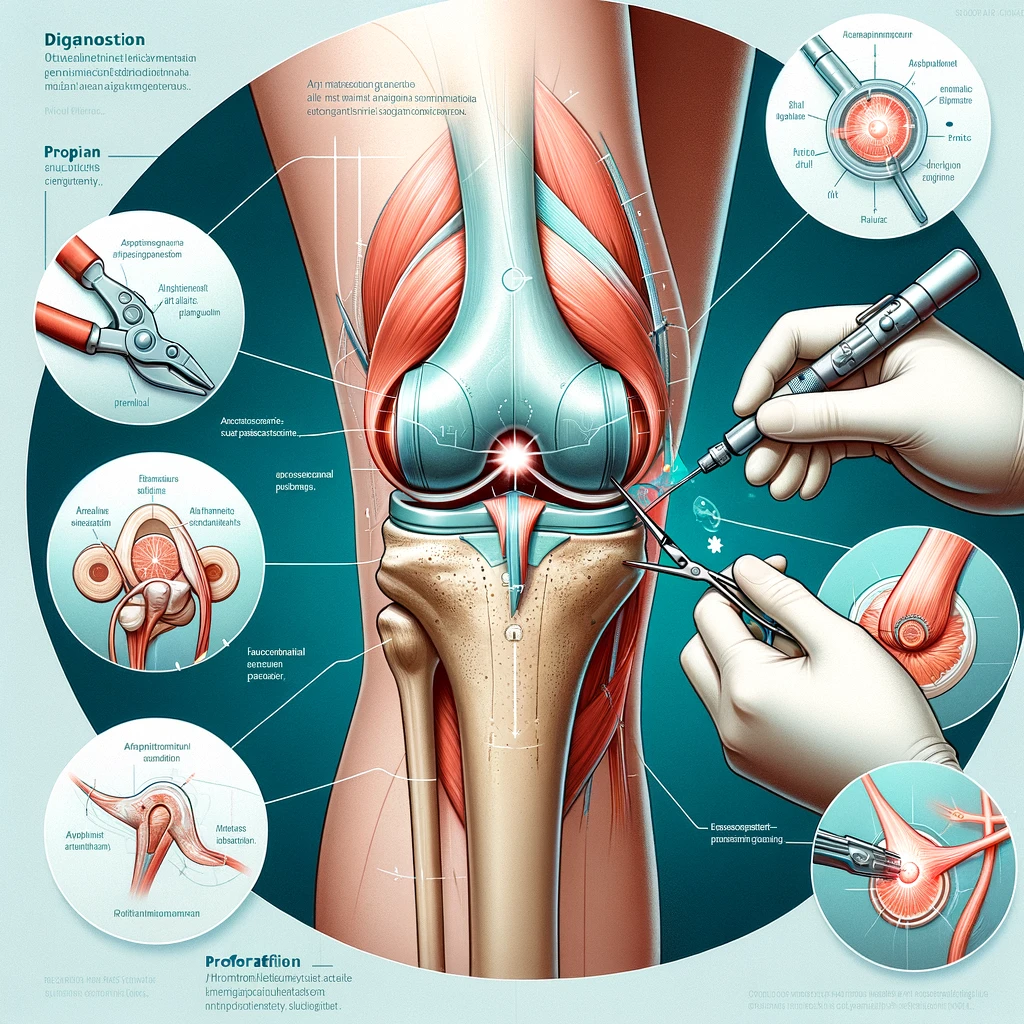
Anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) reconstruction surgery is a complex orthopedic procedure. It involves surgically removing the torn or injured ACL and replacing it with a ‘graft.’ This graft is either taken from tissues of your own body (autograft) or from that of a deceased donor (allograft).
The anterior cruciate ligament is a strong ligament of the knee joint. It runs diagonally in the middle of the bone connecting the thighbone to the shinbone (tibia). It helps stabilize the knee during side-to-side rotation.
The ACL injury may be partial or complete depending on the extent of the damage. It may belong to one of the following three categories:
- Grade I – Injury with partial overstretch of the ACL
- Grade II – Injury with a partial ACL tear
- Grade III – Injury with a complete ACL tear
Types of ACL Reconstruction Techniques
ACL surgeries, when done as outpatient procedures, allow you to go home the same day. Surgeons can use any of the below techniques to perform an ACL reconstruction:
- Arthroscopic ACL reconstruction: This is a minimally invasive method with fewer post-op complications. This approach uses a camera-like device inserted through tiny incisions to access the surgical site easily. The graft is inserted and fixed through tiny incisions.
- No-incision technique: Here, key-hole-sized incisions are made (hence the name no-incision) to access the surgical site, where the surgeon drills small holes into the bone to fix the implant. This is a good technique as this leads to improved knee stability.
- Robotic ACL reconstruction: This is the most advanced surgical technique that uses advanced robotic systems. The robotic arm provides visual accuracy to assist the surgeon in surgery. It has additional benefits such as greater precision, shorter recovery times and better overall results.
- Single-incision technique: This outdated technique uses an endoscope (a medical device consisting of a camera and light attached) to reach the torn ACL. It is no longer used as it leads to certain disadvantages like- more pain, discomfort, trauma, and inappropriate reference point for graft placement. .
- Two-incision technique: Large incisions are made around the surgical site, along with the drilling of large holes in the bone to place the graft or implant. This is the least preferred method due to cosmetic reasons and a long recovery period.
- Double-bundle technique: The ACL has two bundles, the anterolateral and the posteromedial. This double-bundle approach reconstructs both bundles during the ACL tear and improving overall knee stability. This approach is no longer used since there is an increased risk of postoperative complications like osteoarthritis, and graft failure.
What Does ACL Surgery Look Like?
ACL surgery is usually done as an outpatient procedure, and you may be allowed to go home the same day or may be required to stay in the hospital for one or two days. The arthroscopic approach is preferred since it causes less scarring, bleeding, and postoperative complications than traditional open surgical approaches. A tiny camera-like device is inserted through small holes or cuts around the knee joint for easy access to the surgical site. The graft is inserted through these holes and fixed. This approach facilitates faster recovery and restoration of knee function.
What Are The Indications of ACL Surgery?
ACL injuries are most common among athletes who are involved in high-impact sports and activities. Thefollowing indications show that you need ACL reconstruction surgery:
- Grade III ACL tears- When grade 3 tears are present along with a complete ligament tear.
- Sports Injury- During high-impact sports or activities, ACL can be torn due to twisting or cutting movements or sudden changes in direction.
- Unstable knee – A torn ACL with significant functional instability of the knee that limits your daily routine activities also requires surgery for the ACL.
- Associated injuries – When the ACL is torn, there is a risk of damage to other knee structures, such as the joint capsule, menisci, articular cartilage, and other ligaments. In such cases, surgery is done to prevent these risks.
- Growth plate injury- The growth plate is the weakest part of the growing skeleton, and a break due to an injury causes continuous pain. This occurs in children and adolescent patients, which leads to bone growth problems.
People who are very active require surgery to return to their usual activities. Also, people with persistent pain will require one. The need for ACL reconstruction further depends on your lifestyle and occupation. For example, if your job requires manual labor, you are more likely to get the surgery done.
Procedure Involved In ACL Surgery
ACL surgery restores knee stability and functionality after a ligament tear. The remnants of the torn ligament are removed and replaced with the ligament from your body or the tissue of a deceased donor. Let us explore the procedure and the step-by-step treatment of ACL injury.
- Pre-procedure (before the surgery)
- Your doctor will discuss your medical history, the current medications you are taking, and any history of allergies.
- Your doctor will perform a thorough physical examination to assess your knee stability and flexibility.
- S/he will inform you about the procedure and its risks.
- If you are already under some medications, you will be advised to stop some medications (like blood thinners, to prevent the formation of clots) or to adjust the dosage of other medications a few days before the procedure.
- Your doctor will instruct you to follow a prescribed diet for a week before surgery.
- You will be asked to quit smoking and avoid alcohol a week before the surgery as it may interfere with the anesthetic drugs during the procedure.
- You will be advised to fast for a minimum of 8 to 10 hours before your surgery and asked to stop your medications just before the surgery.
- Your anesthesiologist will explain the type and duration of anesthesia administration and its possible side effects.
- You will be given an enema beforehand, which empties the bowels and makes the surgery successful.
- You will be asked to arrange for a family member to drive you home as it is an outpatient procedure.
- Procedure (during the surgery)
- You will be administered general anesthesia (you will be asleep throughout the procedure), usually through an IV (intravenous) line.
- Currently, many surgeons prefer the arthroscopic approach for ACL reconstruction, in which tiny incisions are made around the surgical site.
- A small camera-like device is inserted through one of the incisions to gain access to the surgical site.
- Instruments are inserted through other incisions to remove the torn ACL.
- The graft is inserted and accurately positioned through sockets or tunnels drilled into your femur and tibia.
- The graft is secured to the bone through screws.
- The incision is sutured and bandaged, preferably with a waterproof dressing.
- Post-Procedure (After the surgery)
- In hospital
- You can go home the same day once you recover from the effect of anesthesia, given the procedure is an outpatient one. Otherwise, you may have to stay back for a day or two.
- Your physical therapist (PT) will make you walk on the same day with the help of walking aids like crutches.
- You will be prescribed a knee brace to protect your operated knee from re-injury.
- Your doctor will prescribe pain medications that will provide relief.
- Your PT will demonstrate exercises for knee strengthening, extension (straightening), and flexion (bending) exercises to be followed throughout your recovery period.
- At home
- Around 2 weeks post-surgery, pain and swelling will decrease gradually. You can discontinue your pain medications if you do not have pain.
- Swelling around your knee may be present and can be easily managed by the R.I.C.E therapy
- Rest
- Ice packs
- Compression wraps
- Elevating your leg
- You should follow a proper sleep pattern with a suitable sleep position.
- You should consume a nutritious diet that promotes healing.
- Around 3 weeks post-surgery, you will be able to walk without the help of crutches and resume your daily routine activities.
- By week 6 you can resume driving. You should focus on regaining the range of motion and knee stability during this stage.
- You should continue the exercises as recommended by your PT.
- By 3 months post-surgery, you can resume activities like jogging, swimming, and cycling on the road.
- You may be advised to wear the knee brace for at least 1-year post-surgery to prevent re-injury.
- After their surgeon’s advice, athletes can return to sports around 12 months post-surgery.
- In hospital
What Are The Complications of ACL Surgery?
ACL surgeries have an 80 to 90% success rate, yet you may experience some complications. While infection, allergic reaction to medicines, shock, breathing issues, and trouble peeing are general risks from any surgery, risks specific to ACL reconstruction are the following:
- Anesthesia-related complications
These complications will be present immediately after waking up from anesthesia and will subside in a few hours with medications.
- Itching, redness, and bruising around the surgical site.
- Allergic reactions like hives, itchy skin, shortness of breath, cough, and swelling around your eyes and lips.
- Nausea and vomiting.
- Anterior knee pain
- It is the most common complication which causes pain around the kneecap.
- Mostly seen when a patellar tendon graft is used.
- Stiffness (arthrofibrosis)
- Sometimes a ball of scar may form in front of the knee, known as cyclops lesions
- This limits the straightening of the knee.
- Joint instability
- Happens due to a surgical error.
- Stretching of the graft
- This generally happens due to a surgical error or an undiscovered injury in or around the knee at the time of the ACL tear.
- Ganglion cyst formation
- It is a rare complication.
- Symptoms include knee pain, clicking sound, reduced knee extension, and stiffness.
- Excessive bleeding
- This could be due to injury to the underlying artery during the surgery.
- Formation of blood clots like DVT (deep vein thrombosis)
- This could be due to increased blood pressure or prolonged operating time.
- Growth plate injury
- Commonly occurs in adolescents
- This leads to bone growth problems.
Prognosis of ACL surgery
Successful ACL reconstruction combined with focused rehabilitation and physical therapy can restore your operated knee’s stability, flexibility, and function. If the rehab process is followed correctly, around 90% regain full knee function. ACL reconstructions have an 80 to 90% success rate. Rehabilitation and physical therapy help you resume your daily routine activities in 3 to 6 months post-surgery. However, it may take up to 12 months for athletes to return to sports.
Takeaway
The arthroscopic approach is widely used among orthopedic surgeons currently, owing to fewer post-op complications. Our panel of expert orthopedic surgeons, physical therapists and other healthcare professionals at Medfin are dedicated to providing healthcare services with positive outcomes.
Also Read: The Best Orthopaedic Surgeons in Bangalore
Cost of ACL repair surgery in Bangalore
Disclaimer: The content on this site is the copyright of Medfin and is intended for informational and educational purposes only. This should not be considered as a substitute for medical and surgical expertise. Results from any treatments or surgeries are subjective to an individual patient and the type of procedure/surgery performed. Please seek professional help regarding any medical concerns. Medfin will not be responsible for any act or omission arising from the interpretation of the content present on this page.
CATEGORIES
- ACL Reconstruction
- Anal Fissures
- Anal Fistula
- Appendicitis
- ASK A DOCTOR
- Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia
- Breast Lump Excision
- Cataract
- Circumcision
- Conditions & Diseases
- Cosmetology
- Covid-19
- Cure
- Endocrinology
- ENGLISH VIDEOS
- Eye Care
- Gallstones
- General Surgeries
- Government Schemes
- Gynaecology
- Gynecomastia
- Gynecomastia
- Health
- Health Insurance
- Hernia
- hindi
- Hip Arthoscopy
- Hip Replacement
- Hip Replacement Surgery
- Hydrocele
- Kannada
- Kidney Stones
- Knee Arthroscopic
- Laparoscopic
- LASER
- Latest Treatments
- Lifestyle
- Liposuction
- Medfin Stories
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedic
- Paraphimosis
- Patient Testimonials
- PCL Reconstruction
- Phimosis
- Piles (Hemorrhoids)
- Pilonidal Sinus
- Proctology
- Prostate Artery Embolization
- Rhinoplasty
- Second Opinion
- Total Knee Replacement
- Uncategorised
- Urology
- uterine artery embolization
- Uterine Fibroids
- Varicocele
- Varicose Veins
- Vascular
- VIDEOS






