Total Knee Replacement
Knee Osteoarthritis Causes, Symptoms, Treatments and Know the Warning Signs
by admin
24th August 2023
6 minutes read
Osteoarthritis (OA) is one of the most common chronic conditions of the joints, and the knee is a commonly affected area. If you’re experiencing a ‘painful knee,’ it might be due to osteoarthritis, and understanding the warning signs can help you seek timely ‘knee pain treatment.’
Understanding Knee Osteoarthritis
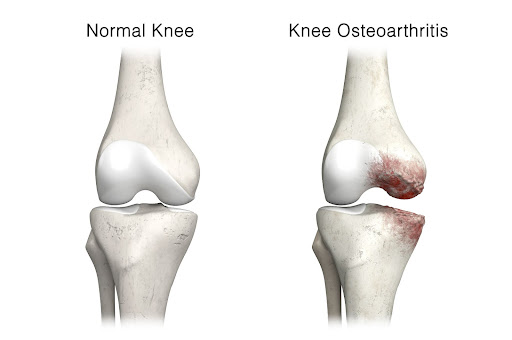
Knee osteoarthritis (OA) is a degenerative joint disease that primarily affects the cartilage, the smooth, cushioning tissue that lines the surfaces of the bones in the knee joint. In a healthy knee, cartilage helps to facilitate smooth movement by reducing friction and acting as a shock absorber.
In knee osteoarthritis, the cartilage breaks down and wears away, causing the bones to rub together. This can result in pain, stiffness, swelling, and a loss of movement in the knee joint. Over time, the joint can change shape and the bones can develop abnormal growths called osteophytes or bone spurs.
Risk factors for knee OA include age, obesity, previous knee injury, overuse of the knee, genetic factors, and other diseases that affect joint health, such as rheumatoid arthritis and metabolic disorders. Symptoms of knee osteoarthritis often develop slowly and worsen over time. They may include knee pain, stiffness and a decreased range of motion. Knee osteoarthritis is typically diagnosed with a combination of a patient’s medical history, physical examination, and imaging tests like X-rays or MRI.
Treatment for knee osteoarthritis usually includes a combination of lifestyle modifications (like weight loss and physical therapy), medications to manage pain and inflammation, and in more severe cases, surgery.
Recognizing the Warning Signs or Symptoms of knee osteoarthritis
There are several key ‘arthritis symptoms to watch out for that could indicate the presence of knee osteoarthritis:
Pain: The ’cause of painful knees’ in osteoarthritis is due to the loss of cartilage and increased friction between the bones. This pain usually worsens after activity or towards the end of the day.
Stiffness: You may notice difficulty with movement after waking up or sitting for extended periods. This stiffness usually lasts for less than thirty minutes and is often described as a feeling of the joint being “locked” or “stuck.”
Swelling: ‘Osteoarthritis knee swelling’ is a common symptom and can occur after prolonged periods of activity. ‘Treatment for knee swelling’ can include rest, ice, compression, and anti-inflammatory medications.
Loss of Mobility: As osteoarthritis progresses, you may experience a decreased range of motion in the knee, making it difficult to perform daily activities like walking, climbing stairs, or getting in and out of chairs.
Crepitus: This is a sensation of crunching or grating within the knee during movement. It is the result of roughened, worn-out cartilage and exposed bone surface rubbing together.
Deformity: In advanced stages of knee osteoarthritis, visible changes to the shape of the knee might be noticeable, such as bowing in or out.
Finding Relief
It’s important to remember that ‘knee pain relief’ is possible. Treatment for osteoarthritis in the knee aims to reduce pain, improve function, and slow the progression of the disease. A combination of treatments is often used, including:
Medication: ‘Knee pain medicine’ and ‘knee joint pain medicine’ are usually the first line of treatment. This can include over-the-counter pain relievers and anti-inflammatory drugs, or prescription medication for more severe pain.
Physical Therapy: Working with a physical therapist can help improve strength, flexibility, and balance, which can relieve pain and prevent further joint damage.
Weight Management: Maintaining a healthy weight can reduce stress on the knee joint, slowing the progression of OA and improving mobility.
Assistive Devices: The use of aids like braces, canes, or shoe orthotics can help alleviate pressure on the knee joint and improve stability.
Surgery: If conservative treatments fail to provide relief, surgical options like knee replacement or joint-preserving surgery may be considered.
How to Prevent Knee Osteoarthritis?
There are several strategies you can adopt to reduce your risk of developing knee osteoarthritis, or to slow its progression if you already have it. Here are some general guidelines:
- Maintain a Healthy Weight: Being overweight puts extra strain on your knees, which can accelerate cartilage breakdown. By maintaining a healthy weight, you can reduce the amount of pressure on your knees and decrease the risk of osteoarthritis.
- Regular Exercise: Regular low-impact exercise helps to strengthen muscles and improve joint flexibility. Consider activities like swimming, cycling, or walking which are gentle on the knees. Strength training, especially for the muscles surrounding the knee like the quadriceps, can also be helpful.
- Avoid Repetitive Stress on the Knees: High-impact activities and repetitive or hard pounding exercises can put extra stress on the knee joints. If your job or sport puts a lot of stress on your knees, protective gear, correct technique, and proper shoes may help protect your joints.
- Healthy Diet: While there’s no specific diet to prevent knee osteoarthritis, a healthy diet that helps maintain a healthy weight is beneficial. Some research also suggests that a diet rich in vitamins C and D, and omega-3 fatty acids may help protect joint health.
- Don’t Ignore Knee Injuries: If you experience a knee injury, seek prompt medical attention to ensure it’s properly treated and fully heals. Properly managed injuries are less likely to lead to arthritis later on.
- Quit Smoking: Smoking can increase the risk of osteoarthritis, among other health problems. Quitting smoking can improve your overall health and may reduce the risk of osteoarthritis.
Remember, while these measures can reduce the risk, they cannot completely eliminate it, especially if you have a genetic predisposition to the condition. If you’re concerned about knee osteoarthritis, it’s a good idea to discuss this with your healthcare provider.
Knowing is Half the Battle
The ’cause of osteoarthritis’ is often multifactorial, including age, genetics, obesity, injury, and overuse. While you can’t change some risk factors, others, like weight and activity level, are within your control. Early detection and treatment can slow the progression of osteoarthritis and improve your quality of life. If you’re experiencing any ‘osteoarthritis signs and symptoms,’ don’t ignore them. Schedule an appointment with your healthcare provider to discuss your ‘knee pain treatment’ options. Remember, you’re not alone in this journey, and help is available.
How Can Medfin Help?
Medfin takes the hassle out of the equation, allowing you to concentrate on your health during Knee Osteoarthritis treatment. We streamline the process, ensuring a stress-free experience so you can prioritize your well-being. Trust Medfin for a smoother journey toward managing and treating Knee Osteoarthritis.
CATEGORIES
- ACL Reconstruction
- Anal Fissures
- Anal Fistula
- Appendicitis
- ASK A DOCTOR
- Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia
- Breast Lump Excision
- Cataract
- Circumcision
- Conditions & Diseases
- Cosmetology
- Covid-19
- Cure
- Endocrinology
- ENGLISH VIDEOS
- Eye Care
- Gallstones
- General Surgeries
- Government Schemes
- Gynaecology
- Gynecomastia
- Gynecomastia
- Health
- Health Insurance
- Hernia
- hindi
- Hip Arthoscopy
- Hip Replacement
- Hip Replacement Surgery
- Hydrocele
- Kannada
- Kidney Stones
- Knee Arthroscopic
- Laparoscopic
- LASER
- Latest Treatments
- Lifestyle
- Liposuction
- Medfin Stories
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedic
- Paraphimosis
- Patient Testimonials
- PCL Reconstruction
- Phimosis
- Piles (Hemorrhoids)
- Pilonidal Sinus
- Proctology
- Prostate Artery Embolization
- Rhinoplasty
- Second Opinion
- Total Knee Replacement
- Uncategorised
- Urology
- uterine artery embolization
- Uterine Fibroids
- Varicocele
- Varicose Veins
- Vascular
- VIDEOS






